,文章字数在1000字左右
html
High Dew Point Conditions and Their Impact on Weather Patterns
Weather patterns are influenced by a multitude of factors, and one of the most significant yet often overlooked is the dew point. The dew point is the temperature at which air becomes saturated with water vapor, leading to condensation. When the dew point is high, it indicates a substantial amount of moisture in the air, which can have profound effects on weather conditions, human comfort, and even infrastructure. This article explores high dew point conditions, their causes, and their broader impact on weather systems.
Understanding Dew Point
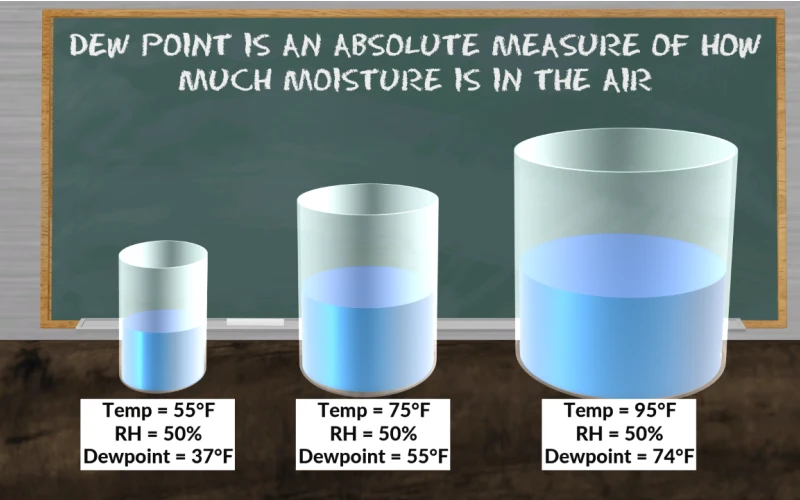
Dew point is a critical metric in meteorology because it provides a direct measure of atmospheric moisture. Unlike relative humidity, which fluctuates with temperature, the dew point remains constant unless the actual moisture content of the air changes. A high dew point, typically above 65°F (18°C), signifies humid conditions, while a low dew point indicates drier air. When the air temperature approaches the dew point, fog, dew, or precipitation can form, depending on other atmospheric conditions.
Causes of High Dew Point Conditions
Several factors contribute to high dew point conditions:
- Proximity to Water Bodies: Regions near oceans, lakes, or rivers often experience higher dew points due to increased evaporation.
- Warm Air Masses: Warm air can hold more moisture than cold air, so tropical or subtropical air masses often bring high dew points.
- Agricultural and Vegetative Activity: Areas with dense vegetation or irrigation can release moisture into the air through transpiration, raising the dew point.
- Urban Heat Islands: Cities with limited green spaces and high concrete coverage can trap moisture, leading to elevated dew points.
Effects on Weather Patterns
High dew point conditions play a pivotal role in shaping weather systems. Some of the most notable impacts include:
1. Increased Precipitation
When the dew point is high, the atmosphere contains ample moisture, which can lead to heavy rainfall or thunderstorms. This is particularly common in tropical regions where high dew points are the norm. The excess moisture provides the necessary fuel for convective storms, resulting in intense downpours and even flash flooding.
2. Enhanced Heat Index
A high dew point exacerbates the perceived temperature, making hot days feel even more oppressive. The heat index, which combines air temperature and humidity, rises significantly under high dew point conditions. This can lead to heat-related illnesses and increased energy demand for cooling.
3. Fog Formation
When temperatures drop overnight but remain close to the dew point, fog is likely to form. This is especially common in valleys or near water bodies. Dense fog can reduce visibility, disrupting transportation and posing hazards for drivers and pilots.
4. Tropical Cyclone Development
High dew points over warm ocean waters are a key ingredient for tropical cyclone formation. The abundant moisture and latent heat release fuel these storms, contributing to their intensity and longevity.
Human and Environmental Impacts
Beyond weather patterns, high dew point conditions affect daily life and ecosystems:
- Health Risks: High humidity levels can make it harder for the body to cool itself, increasing the risk of heat exhaustion or heat stroke.
- Agricultural Effects: While some crops thrive in humid conditions, excessive moisture can promote fungal growth and plant diseases.</
Keyword: high dew point
Leave a Reply